
Newtons Laws Of Motion
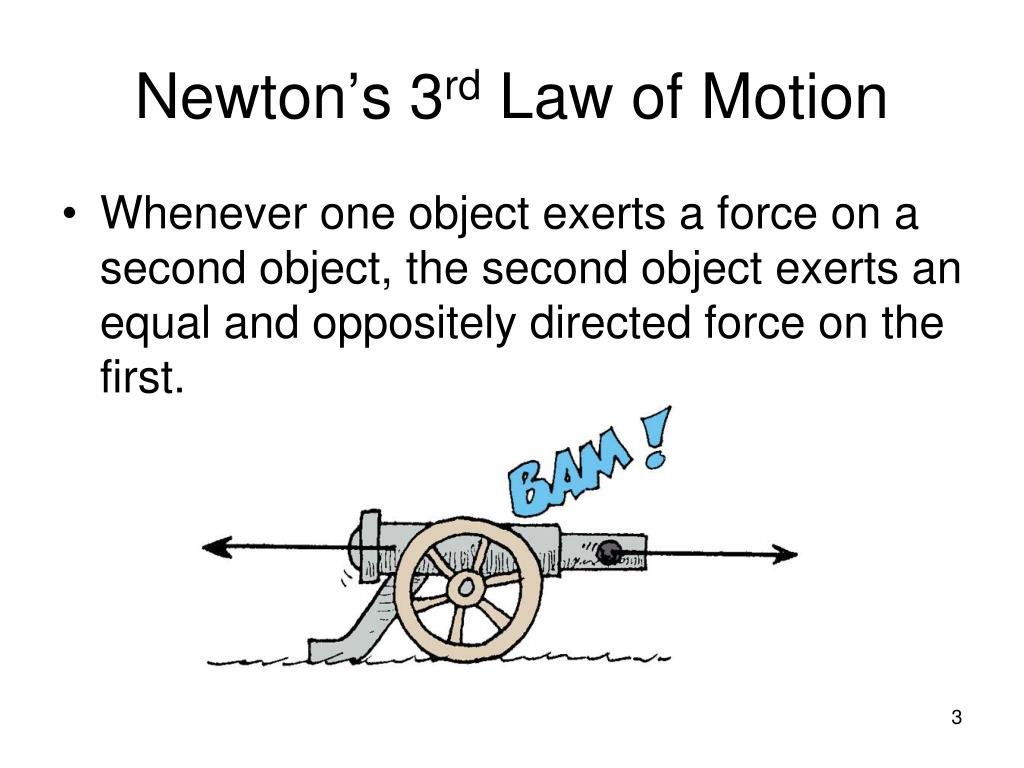
Newton's Third Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. What this means is that pushing on an object causes that object to push back against you, the exact same amount, but in the opposite direction. For example, when you are standing on the ground, you are pushing down.

InsertLearning Share
Chapter 5 PowerPoint slides: "Newton's Third Law of Motion". PowerPoint slides based on Chapter 5 ("Newton's 3rd Law of Motion") of the 'Applied Physics' textbook, "Conceptual Physics", 12th Edition. To print or download this file, click the link below:
PPT Newton’s Laws of Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4506925
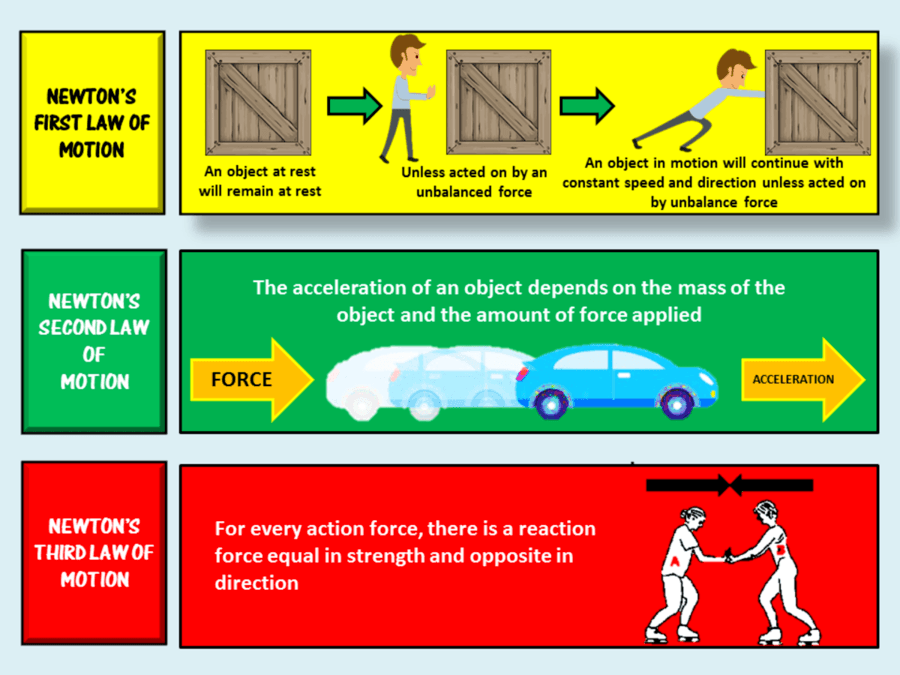
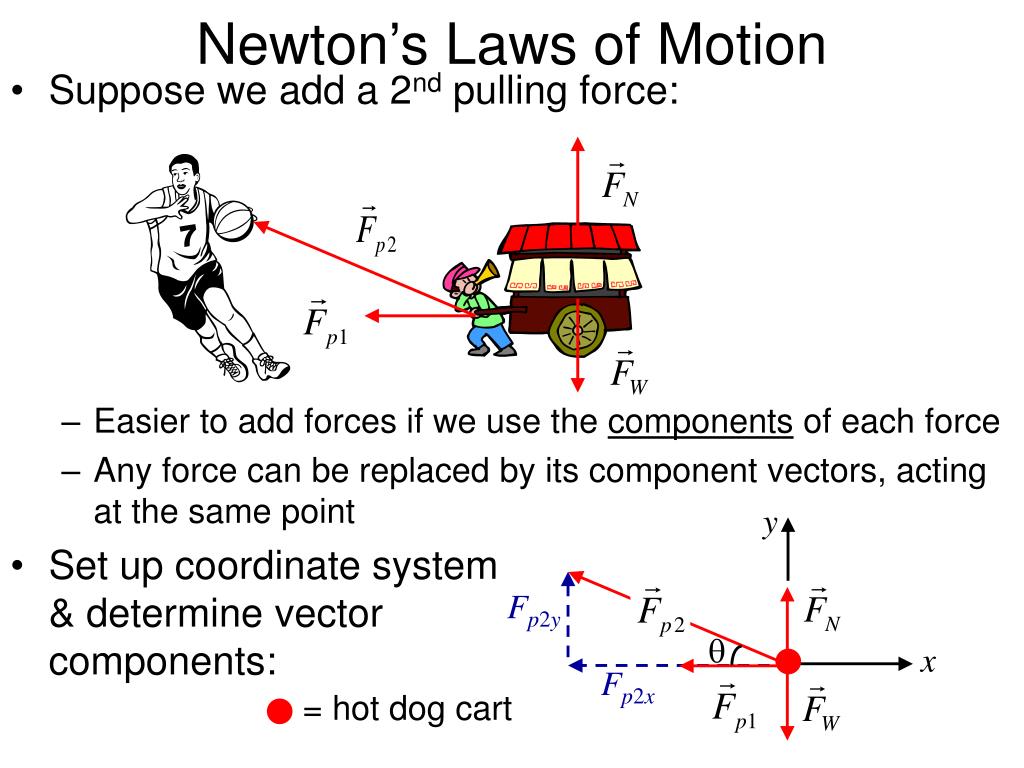
Newton's Laws of Motion 0 1st Law — An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. — Force equals mass times acceleration, — For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction,

Newtons 1st law of motion Laws of Motion Quiz Quizizz
3. Newton's Laws of Motion add to notes Newton's First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton's Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton's Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Section 4 Newton’s Laws of Motion Nitty Gritty Science
Lesson 4: Newton's Laws of Motion. 4.1 Newton's First and Second Laws. 4.2 Newton's Third Law. 4.3 Reference Frames. 4.4 Non-inertial Reference Frames.
PPT 5 Newton’s Third Law of Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID457661
For every force acting on an object, there is an equal force acting in the opposite direction. Right now, gravity is pulling you down in your seat, but Newton's Third Law says your seat is pushing up against you with equal force. This is why you are not moving. There is a balanced force acting on you- gravity pulling down, your seat pushing up.

4 Newton's Second Law of Motion
PowerPoint slides based on Chapter 2 ("Newton's 2nd Law of Motion") of the 'Applied Physics' textbook, "Conceptual Physics".
PPT Sir Isaac Newton & The Three Laws of Motion PowerPoint Presentation ID6695637
The weight always acts downwards, toward the center of the earth. The SI unit of force is the Newton (kg∙m/s2) The SI symbol for the Newton is N. If you know the mass (kg) of something and want its weight in Newton's at Earth's surface, multiply the number of kilograms. by 9.81 m/s2. Note - The units for mass must be in kg so be careful.

6th Grade Science 4th Six Weeks (Wk 5) Motion & Forces Review & Assessment
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Newton was a scientist that changed the history of physics. He came up with three laws that could describe how the objects around us move and interact with each other, and they're super easy to understand, as long as you use visual representations of the forces. This template offers exactly that!

PPT Newton’s Laws of Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2099271
Newton's Laws of Motion Overview PowerPoint Slides. This resource is designed to be used with the Exploring Force and Motion Project-Based Learning Unit. It includes overview information for Newton's 3 Laws of Motion. This resource can be used in conjunction with the Exploring Force and Motion Lesson Plan included with the project-based.

Newton's Laws of Motion Learning Chart, 17" x 22" T38054 Trend Enterprises Inc. Science
Newton's Second Law in One Dimension Using Newton's 2nd Law to Solve Problems Identify all forces acting on the object -Pushes or Pulls -Frictional forces -Tension in a string -Gravitational Force (or weight = mg where g is 9.8 m/s2) - "Normal forces" (one object touching another). Draw a "Freebody Diagram" -draw the object, show.

PPT Newton's Laws of Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4737308
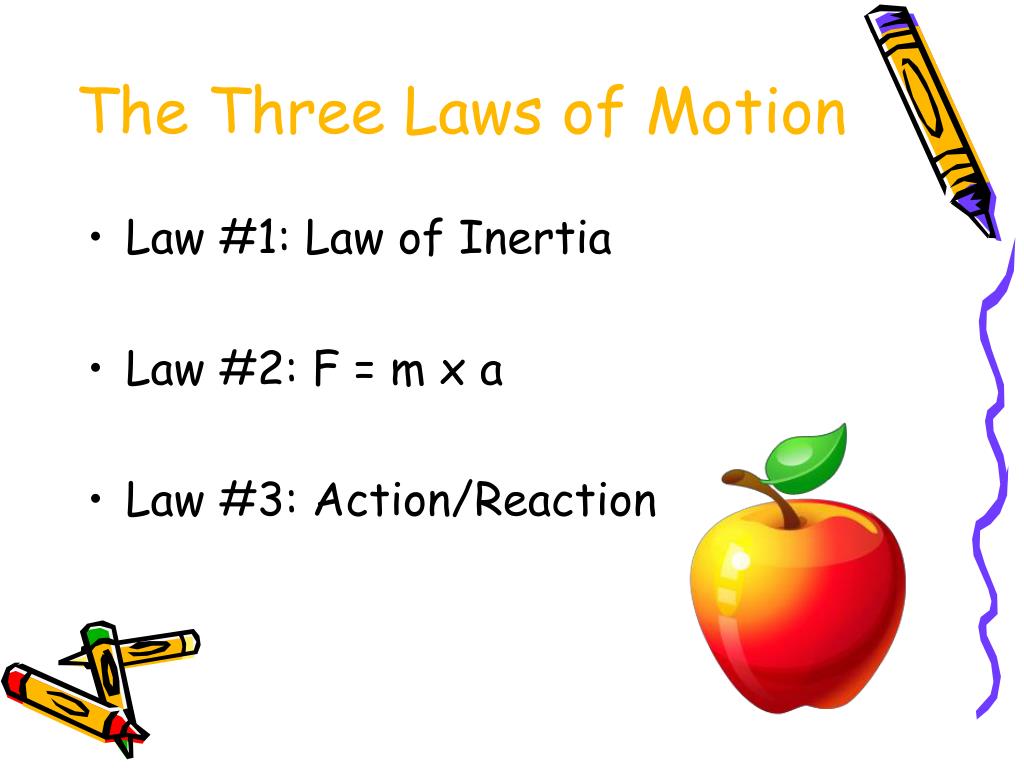
Introduction • Newtons 3 laws of motion • 1. Law of inertia • 2. Net Force = mass x acceleration • ( F = M A ) • 3. Action Reaction • Newton's Universal Law of Gravity. Isaac Newton 1642-1727 Isaac Newton 1689 Knighted by Queen Anne 1705 Isaac Newton 1702 Isaac Newton 1726.

Newton's Laws Of Motion Passnownow
Learn the basics of Newton's First Law of Motion, also known as the law of inertia, in this PowerPoint presentation. You will see examples of how objects resist changes in their state of motion and how forces affect them. This is the second chapter of the 'Applied Physics' textbook, "Conceptual Physics", 12th Edition.

Newton’s Laws of Motion by Daenna González Issuu
Newtons Laws Of Motion. 1. Newton's Laws of Motion Adapted from free PowerPoint slides found at. If mass remains. 31. 32. 33. Newtons Laws Of Motion - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
PPT Newton’s Laws of Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4506925
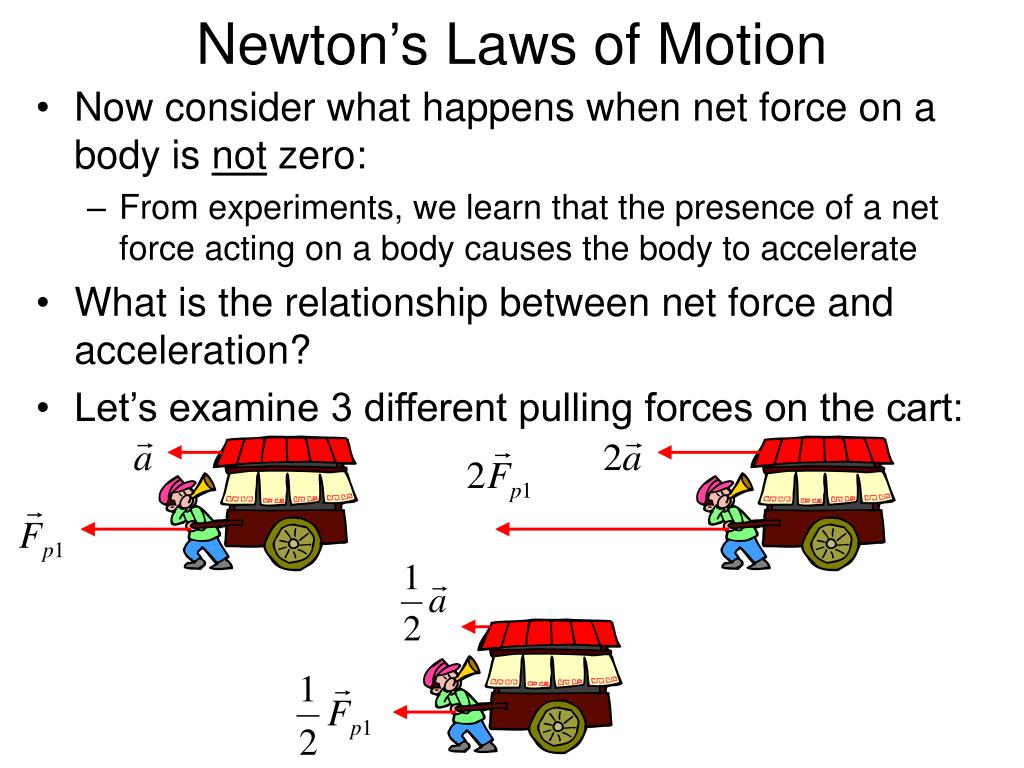
Newton's Laws of Motion • Magnitude of acceleration is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force acting on the body • Constant of proportionality is the mass m of the body • Newton's 2nd Law: or • In (2 - D) component form: • Remember that: • Newton's 2nd Law is a vector equation • Newton's 2nd Law refers.
Newton’s laws of motion
7. Newton's Third Law of Motion: Law of Interaction • "For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction." • The difference between the forces related to Law of Interaction and forces in a balanced state are as follows: Action-Reaction Forces Balanced Forces Two forces are equal in size. Two forces are opposite to each other in terms of direction. Two forces have the same.